The Benefits Of Using MyOnlineCampus.com For Fully Online Study
Unlock your full potential with MyOnlineCampus.com – the ultimate platform for fully online education.
Read More
By: Michelle Kruger
Gen Z, born roughly between 1997 and 2012, is a generation that has grown up in the digital age, surrounded by technology and social media. As such, their learning style is influenced by their use of technology and their exposure to a constant stream of information.
Just to put this generation in perspective, for me as a millennial, having computers in the classroom was cool and new, for Gen Z it is beginning to grow old.
Millennials are known for their proactive approach to seeking information compared to previous generations. On the other hand, Gen Z has grown up in a world where they are constantly bombarded with information from various sources. They are used to having information delivered to them in a personalized way, without having to put in much effort. Personalization has become a crucial aspect of Gen Z's learning experience, where they expect to receive content that is tailored to their interests and needs. As a result, incorporating personalized learning strategies into teaching can help keep Gen Z students engaged and motivated (Acer for Education, 2019).
Gen Z and Millennials are two distinct generations with some notable differences in their attitudes, behaviours, and values. It will be helpful to look at some key differences that set Gen Z apart from Millennials:
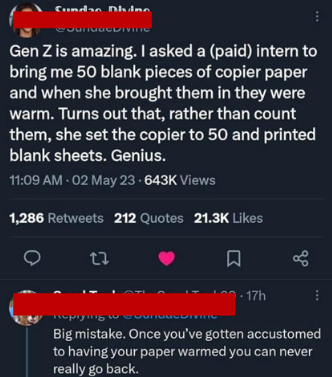
Image: Instagram
These are just a few of the key differences between Gen Z and Millennials. While there are some similarities between the two generations, Gen Z is shaping up to be a unique and influential group that will have a major impact on the world in the years to come.
There are a few “ground rules” for understanding these tech natives and it is very important to truly adapt our pedagogical view of teaching to ensure we do not lose student numbers to the vast domain of free education out there.
Gen Z learns on its own, if there is something they do not know they Google it (and they make use of the word Google as a verb). That is not to say that they do not need teachers. They are overflown with an abundance of information daily, and without proper guidance, they will not learn and master the essence of the subject. The numbers support this: 39% of Gen Zs prefer to learn with the guidance of a teacher whereas the Millennial generation only 25% prefer guidance from a teacher (Acer for Education, 2019).
They are “The Tech-Savvy Generation”, harnessing the Power of AI and Digital Tools to Enhance Learning – thus an emphasis on the importance of technology and digital tools in the education of Gen Z students. They are SUPER comfortable with technology and expect to use it in their learning. AI and other digital tools can enhance their educational experience and keep them engaged in their learning journey (Krishna, S. 2021).
Teaching to the Next Generation, we need to understand them and adapt our andragogy – emphasis on the need to understand the unique characteristics and learning preferences of Gen Z students and adapt teaching styles accordingly. For starters, it is crucial to build relationships with these students, provide experiential learning opportunities, and create a student-centred, safe online environment (EdTech Magazine, 2019).
Adapting Your Teaching Style for Gen Z Students: Focus on the fact that Gen Z students represent the future of education and that we as educators must adapt our teaching styles to prepare these students for the challenges of the 21st century. 21st-century skills include teaching critical thinking, problem-solving, and digital literacy skills, the role of technology and digital tools in preparing Gen Z students for the future workforce (EDUCASE, 2022).
Characteristics of how Gen Zs learn
Overall, collaboration activities for Gen Z university students involve providing opportunities for teamwork, communication, and critical thinking and can help students develop skills that are valuable in both academic and professional contexts.
Gen Z students generally have a shorter attention span than previous generations and therefore may benefit from shorter, more focused lectures. Research suggests that the ideal length for a lecture or presentation is between 10-20 minutes, as this is the amount of time that most people can effectively concentrate and retain information.
However, it's important to note that the length of a lecture should ultimately depend on the content being presented and the needs of the students. If the material requires more time to cover in-depth, it may be appropriate to extend the lecture. Conversely, if the material is simple or straightforward, a shorter lecture may be more effective.
To keep Gen Z students engaged, it's also important to incorporate interactive and experiential learning opportunities into lectures, such as group activities, discussions, and hands-on projects. This can help break up the lecture and provide opportunities for students to apply what they have learned in a practical and engaging way (Manasrah, A. et al., 2021).
Authentic and relevant learning experiences for Gen Z students involve providing opportunities for hands-on, experiential learning, incorporating real-world problems and scenarios, and using technology and digital tools to increase engagement and relevance.

Gen Z learns best through interactive and visual experiences that are authentic, collaborative, and self-directed (Schrader, J. 2022).
Question: A higher percentage of Gen Z (39%) prefer to learn with guidance versus the generation of millennials (25%) (Acer for Education, 2019). Although the numbers went up, it is still a “fail”. Can this be because educators have not yet adapted their pedagogical/ pedagogical methods? If this is the case, then a red flag should be popping up in the back of our heads. We need to adapt our teaching method ASAP.
Let’s take a look at some grand examples of online learning activities that are popular among Gen Zs to keep them engaged and focused (Panopto Team, n.d.).

Many Gen Z learners prefer immersive experiences, so virtual reality (VR) learning is becoming more popular. With VR, they can explore new environments, practice new skills, and experience new perspectives (Wertz, 2022). While COVID was devastating, it did allow for some great immersive experiences to see places you might have never seen before, like a virtual tour of a museum in Italy, an Aquarium in Vegas and even 360 panoramas of cities and natural landmarks.
These are just a few examples of the online learning activities that are popular among Gen Z learners and loads more will be invented as we engage more and more with this generation in the years to come.
At the start, I mentioned that it is crucial to ensure you have built a relationship with your students. If you are a Baby Boomer, you might consider changing some communication tactics and learning some slang to ensure this relationship is, for the social part, solid. Slang words like “Glow-up” (meaning someone grew from where they used to be, “Slay”, roughly translated to doing something well, “Bet” meaning yes or OK, and “Vibing” can best be described as you are cool ✌🏻 or you are on fire – fire being a good thing 🤔.
It’s not only the slang words but the communication is way more informal, Emojis and GIFs are standard languages that are fully understandable by them as if they were back in 300 BC drawing images in Tombs.


Images from: BuzzFeed
I imagine them projecting an emoji into the night sky like Batman back and forth to communicate with each other.

Image created by Picsart, an AI Image generator.
Orait, orait, orait! So, let’s see how they communicate.
Gen Z prefers to communicate using a variety of digital and online channels. Here are some common ways that Gen Z prefers to communicate (Dagostino, 2021):
Instant messaging: Gen Z is known for its love of instant messaging. They prefer to communicate using platforms like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, iMessage, and Snapchat. They use these platforms to stay in touch with friends and family, share photos and videos, and send quick messages.
Social media: Social media platforms like Instagram, TikTok, Twitter, and Snapchat are also popular among Gen Z for communication. They use these platforms to share updates, connect with others, and stay informed on current events.
Video conferencing: With the rise of remote work and online learning, video conferencing has become an important way for Gen Z to communicate. Platforms like Zoom, Skype, and Google Meet are commonly used for online meetings, classes, and social events.
Email: Although Gen Z is known for their love of instant messaging, they still use email for more formal or professional communication. Email is still a common way to communicate with teachers, employers, and other professionals.
Emojis and GIFs: Gen Z is known for their use of emojis and GIFs in their digital communication. They use these visual elements to express emotions and convey messages in a more playful and engaging way (thus my Batman signal of emojis in the night sky).
Overall, Gen Z prefers to communicate using digital and online channels that are quick, convenient, and interactive. These are advantageous because in online teaching we communicate digitally as far as possible.
Easy peasy lemon squeezy, just keep them ENGAGED AND MOTIVATED!
But how? How do we keep this generation engaged AND motivated? Below are some ideas paired together, one for engagement along with its companion on motivating them. You can make use of the following in your online course design:
|
Purpose-driven work (Motivated): Gen Z wants to positively impact society. They are motivated by work that has a sense of purpose and meaning, and they want to feel like they are making a difference. Give them a task that addresses these needs, one that allows them to create something or solve a problem of something that matters (to them as well) (Yu et al., n.d.). This then links to what’s next: Make learning relevant (Engaged): Gen Z is motivated by purpose-driven work, and they want to understand how the knowledge they gain will apply to their future careers. Educators can make learning relevant to Gen Z by showing how the material they are learning can be applied in real-world situations (Afshar et al., 2019). |
|
Autonomy and flexibility (Motivated): Gen Z values autonomy and flexibility in their work. They want to have control over their schedules and work on their own terms. They are motivated by the freedom to pursue their passions and interests, and to work in a way that suits their lifestyle (Yu et al, n.d.). So, we Use Technology (Engaged): Gen Z is digital natives who have grown up with technology, and they expect to use it in their learning. Incorporate technology into your teaching, such as using interactive online tools, virtual simulations, and multimedia content (Afshar et al., 2019). |
|
Personal growth (Motivation): Gen Z is a generation that values personal growth and development. They are motivated by opportunities to learn new skills and take on new challenges. They want to feel like they are constantly growing and improving, both personally and professionally (Yu et al, n.d.). Then, let's provide feedback (Engaged): Because Gen Z values personal growth and development they want to know how they are progressing in their learning. You can provide regular feedback and assessments to help Gen Z track its progress and identify areas where they need to improve (Afshar et al., 2019). |
|
Diversity and inclusion (Motivated): Gen Z is a highly diverse and inclusive generation. They are motivated by work environments that celebrate diversity and foster inclusivity. They want to work for companies that prioritise diversity and take meaningful action to create a more equitable workplace (Wondergem, 2017). This means you need to: Be inclusive (Engaged): Gen Z is a highly diverse and inclusive generation, and they expect you as their educator to be as well (Afshar et al., 2019). |
|
Technology and innovation (Motivated): Gen Z is a generation that is highly tech-savvy and innovative. They are motivated by work that involves cutting-edge technology and allows them to be creative and innovative. They want to push the boundaries of what is possible (Liebenberg, n.d.). Encourage collaboration (Engaged): Gen Z is social and collaborative learners who thrive in group settings. Professors can create opportunities for Gen Z to collaborate with their peers, such as group projects, online discussions, and peer-to-peer feedback (Wondergem, 2017). |
Key takeaway
In a nutshell, Gen Z is motivated by work, projects, assignments, tasks and activities that are purpose-driven, flexible and foster personal growth and development. They seek diversity and inclusion and are at the forefront of innovation and technology (Yu et al, n.d.). Technology forms part of their ‘matter’ of existence. To see a Gen Z not making use of technology is like discovering an animal 20 years after declared extinct – possible but rare. And with the influx of new tech tools daily, especially Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools, we might as well jump on board that ship. “The ship is leaving, if you are not onboard, you get left behind.” - King George, Australian Survivor, 2023.

Image created by Gencraft
Something cool to read about: Don’t Ban ChatGPT in Schools. Teach with it (Roose, 2023).
References:
Acer for Education. 2018. Gamification in Education: The future of learning. Available at: https://acerforeducation.acer.com/education-trends/gamification/gamification-in-education-the-future-of-learning/?psafe_param=1&gclid=CjwKCAjw3ueiBhBmEiwA4BhspOCc4bkc-j5FN6awjxEJ0gV-rMXT0IQmO_xoeHu9yH9uLm09i4wTJRoCcywQAvD_BwE
Acer for Education. 2019. Infographic Millennials vs Generation Z: How education is evolving. Available at: https://acerforeducation.acer.com/education-trends/education-technology/infographic-millennials-vs-generation-z-how-education-is-evolving/?gclid=CjwKCAjw3ueiBhBmEiwA4BhspJRVwSNHrQMWa7iFH0kp1nNRQNjvulOMPiltV8KRXA1sowXUBRIKsRoCY60QAvD_BwE
Afshar, M., Jafari, A., Heshmati, F., Movahedzadeh, F., Cherif, A.H. 2019. Instructional Strategies for Motivating and Engraining Generation Z Students in Their Own Learning Process. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/330774868_Instructional_Strategies_for_Motivating_and_Engraining_Generation_Z_Students_in_Their_Own_Learning_Process
Barton, T. 2020. 5 Ways To Integrate Service-Learning Through An Online Learning Approach. Available at: https://servelearn.co/blog/5-ways-to-integrate-service-learning-through-an-online-learning-approach/
Budnike, Z. 2022. Generation Z turn to online learning to sharpen their skills. Available at: https://www.aerotime.aero/articles/32808-generation-z-online-learning-skills
Buecheler, S. 2019. Self-Directed Learning: Train Gen Z How They Want to Learn. Available at: https://www.knowledgeanywhere.com/resources/article-detail/self-directed-learning-train-gen-z-how-they-want-to-learn
Crespo, I. 2023. Podcasting as the Gen-Z medium. Available at: https://www.uscannenbergmedia.com/2023/01/11/podcasting-as-the-gen-z-medium/
Dagostino, A. 2021. Here Is How Gen Z Is Changing The Way We Communicate. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbescommunicationscouncil/2021/08/09/here-is-how-gen-z-is-changing-the-way-we-communicate/?sh=8562a3c13502
Duffy, R. 2018. Gen Z strongly favors learning through YouTube and video, report says. Available at: https://edscoop.com/generation-z-learning-youtube-video-pearson-study/
EDUCAUSE. 2022. Learning Analytics from a Systems Perspective: Implications for Practice. Available at: https://er.educause.edu/articles/2022/2/learning-analytics-from-a-systems-perspective-implications-for-practice
Faust, 2017. This is what Gen Z-designed curriculum looks like for the future. Available at: https://www.eschoolnews.com/classroom-innovations/2017/04/17/gen-z-designed-curriculum/
Fisher, S. 2022. 14 Fre PowerPoint Game Templates. Available at: https://www.lifewire.com/free-powerpoint-games-for-teachers-1358169
Ivec, S. n.d. Creating Branching Scenarios in PowerPoint. Available at: https://getmygraphics.com/blog/creating-branching-scenarios-in-powerpoint/
Krishna, S. 2021. Artificial Intelligence: How To Blend It Into Custom eLearning Development. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/artificial-intelligence-how-to-blend-it-into-custom-elearning-development
Liebenberg, I. The Education Network. n.d. Gen Z – How do we keep them engaged in a learning environment? Available at: https://eduvationnet.co.za/news_article/gen-z-how-do-we-keep-them-engaged-in-a-learning-environment/
Manasrah, A., Masoud, M., Jaradat, Y. 2021. Short Videos, or Long Videos? A Study on the Ideal Video Length in Online Learning. Available at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9491115
Matousek, M. 2020. Elon Musk says you still don't need a college degree to work at Tesla. Here's what he looks for in job applicants instead. Available at: https://www.businessinsider.com/elon-musk-no-college-degree-needed-to-work-at-tesla-2019-12
Maxwell, R. n.d. Why Gen Z could be the answer to declining apprentice numbers. Available at: https://www.verto.org.au/blog/why-gen-z-could-be-the-answer-to-declining-apprentice-numbers
Mc Crindle, M. 2017. How to teach Gen Z to be collaborative, innovative and responsive. Available at: https://blog.google/outreach-initiatives/education/how-teach-gen-z-be-collaborative-innovative-and-responsive/
Miranda, C. 2020. Generation Z: Re-thinking Teaching and Learning Strategies. Available at: https://www.facultyfocus.com/articles/teaching-and-learning/generation-z-re-thinking-teaching-and-learning-strategies/
Mitchell, J., Silver, M. 2019. How to make college more relevant for Gen Z. Available at: https://psmag.com/ideas/gen-z-how-to-make-college-more-relevant
Olipas, C.N. 2022. The Gen Z's Learning Experiences and Its Relationship to Social Media Use. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/361577692_The_Gen_Z's_Learning_Experiences_and_Its_Relationship_to_Social_Media_Use
Pappas, C. 2015. Project-Based Learning In eLearning: What eLearning Professionals Should Know. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/project-based-learning-in-elearning-what-elearning-professionals-should-know
Pappas, C. 2023. Personalized Learning For Gen Z: Transforming Training For The Next Generation Of Employees. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/personalized-learning-for-gen-z-transforming-training-for-the-next-generation-of-employees
Panopto Team. n.d. They’re Coming: Rethinking Training And Development For Generation Z. Available at: https://www.panopto.com/blog/rethinking-training-and-development-for-generation-z/
Roose, K. 2023. Don’t Ban ChatGPT in Schools. Teach With It. Available at: https://www.nytimes.com/2023/01/12/technology/chatgpt-schools-teachers.html
Seibert, A. 2020. Problem-based learning: A strategy to foster Generation Z's critical thinking and perseverance. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1557308720301049
Schrader, J. 2022. How Gen Z Learns: It’s More Self-Paced and Collaborative Than Ever. Available at: https://www.metroparent.com/education/school-issues/how-gen-z-learns/
Vander Linde, R., Weatherly, R. n.d. Engaging Gen Z on Social. Available at: https://www.american.edu/ucm/upload/gen-z_engagement.pdf
Wertz, J. 2022. Generation Z Gravitates Towards Immersive Tech-Driven Experiences. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/jiawertz/2022/11/30/generation-z-gravitates-towards-immersive-tech-driven-experiences/?sh=4587283c5ab6
Wondergem, K. 2017. Here Comes Z: Strategies To Engage A New Generation Of College Students. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/engage-a-new-generation-of-college-students-strategies
Yu, E., Canton, S. n.d. Journal of Educators Online. Student-inspired optimal design of online learning for Generation Z. Available at: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1241579.pdf
Program Totall Fees :
Program Totall Credits :
Program Totall Module :
Don’t miss out, partner with us.